 mutation, an alteration in the genetic material (the genome) of a cell of a living organism or of a virus that is more or less permanent and that can be transmitted to the cell’s or the virus’s descendants.
mutation, an alteration in the genetic material (the genome) of a cell of a living organism or of a virus that is more or less permanent and that can be transmitted to the cell’s or the virus’s descendants. In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. [1] Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA.
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. [1] Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA.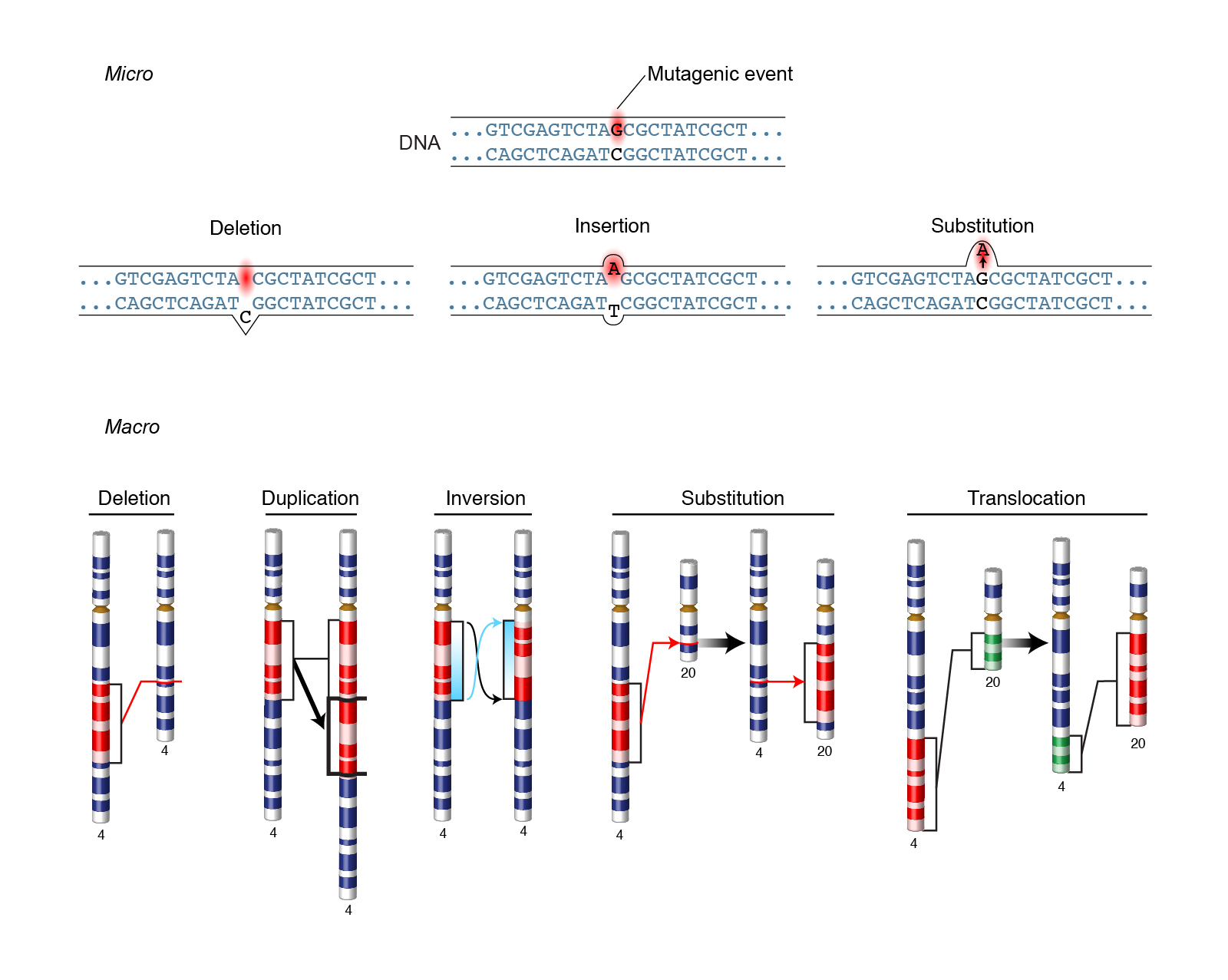 A mutation is a change in a DNA sequence. Mutations can result from DNA copying mistakes made during cell division, exposure to ionizing radiation, exposure to chemicals called mutagens, or infection by viruses.
A mutation is a change in a DNA sequence. Mutations can result from DNA copying mistakes made during cell division, exposure to ionizing radiation, exposure to chemicals called mutagens, or infection by viruses.